-
Cangzhou Yulong Steel Co., Ltd.
-
Phone:
+86 13303177267 -
Email:
admin@ylsteelfittings.com
- English
- Arabic
- Italian
- Spanish
- Portuguese
- German
- kazakh
- Persian
- Greek
- French
- Russian
- Polish
- Thai
- Indonesian
- Vietnamese
- Zulu
- Korean
- Uzbek
- Hindi
- Serbian
- Malay
- Ukrainian
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Miao
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- igbo
- irish
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Kannada
- Khmer
- Rwandese
- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- China
- China (Taiwan)
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Norwegian
- Occitan
- Pashto
- Dutch
- Punjabi
- Romanian
- Samoan
- Scottish Gaelic
- Sesotho
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Tatar
- Telugu
- Turkish
- Turkmen
- Urdu
- Uighur
- Welsh
- Bantu
- Yiddish
- Yoruba

Sep . 24, 2024 21:42 Back to list
1 1 4 threaded coupling
Understanding 1% 201% 4% Threaded Coupling in Mechanical Engineering
Threaded coupling is a crucial element in mechanical engineering, facilitating the connection between parts in a secure and efficient manner. Among the various types of threaded coupling, the specific designations such as 1% 201% 4% threaded coupling can have implications in manufacturing and assembly processes. This article explores the features, applications, and benefits of this particular threaded coupling configuration.
What is Threaded Coupling?
Threaded coupling is a method of connecting two or more components using threads. The threads create a secure mechanical bond that can bear significant loads and stresses. In engineering designs, the choice of coupling type largely depends on the application’s requirements, such as strength, flexibility, and ease of assembly.
The Significance of 1% 201% 4% Designation
The designation of 1% 201% 4% refers to a specific categorization within threaded couplings which typically indicates percentage values related to certain parameters of the coupling. Such values can refer to factors like material strength, diameter, and load capacity, though the specifics can vary depending on industry norms and applications. Understanding these percentages is crucial for engineers to select the optimal coupling for their designs.
Applications of Threaded Coupling
Threaded couplings are widely used across various industries. In the automotive sector, they facilitate the assembly of engines and transmission systems, ensuring that components remain connected under vibration and load. In the construction industry, threaded couplings are essential for securing structural elements, allowing for flexible yet robust connections among beams and columns.
1 1 4 threaded coupling
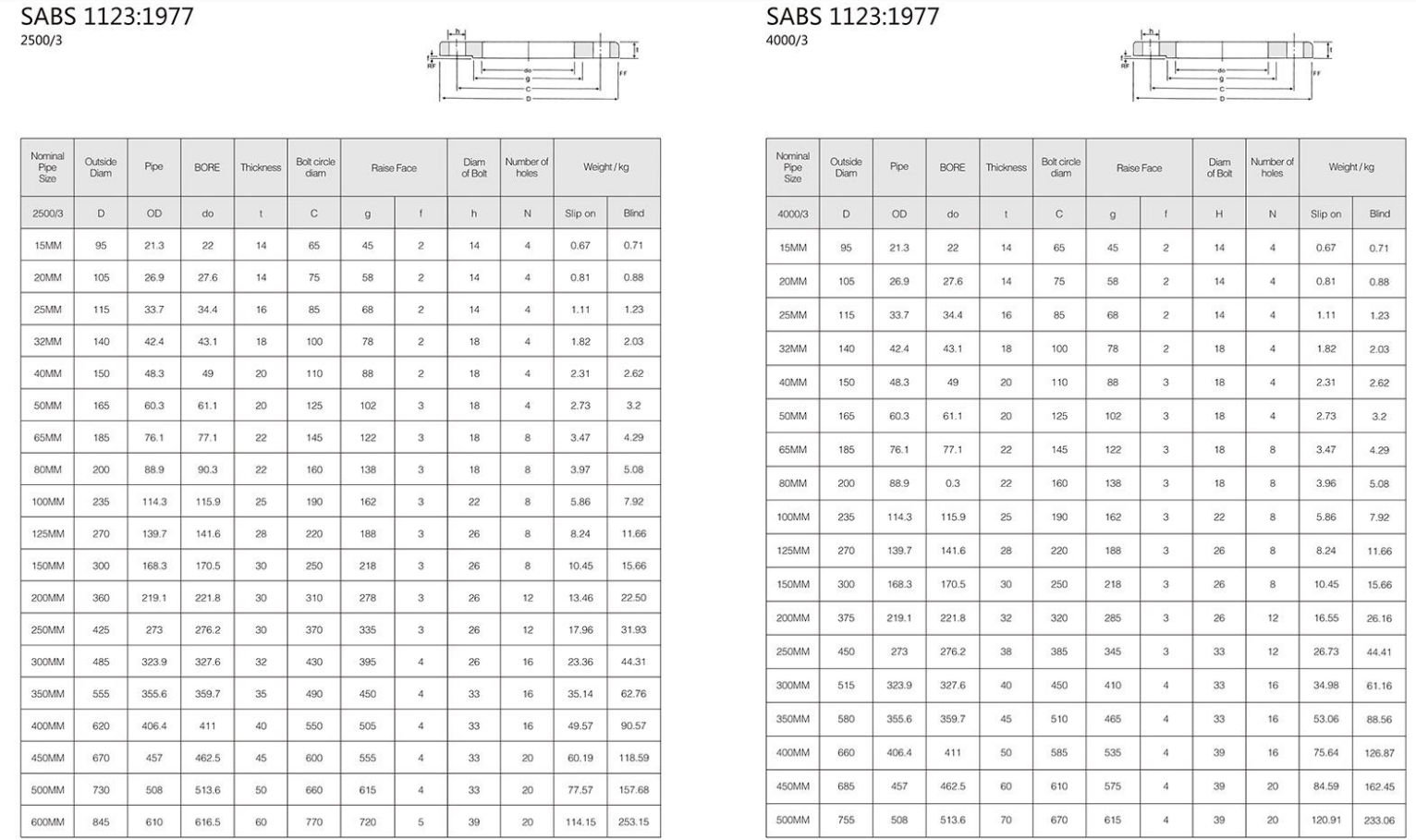
In plumbing and fluid systems, threaded couplings play a vital role in ensuring leak-proof and secure connections between pipes. Their reliability in high-pressure environments is paramount, making them indispensable in many engineering applications. The 1% 201% 4% designation can also imply the specific application context, suggesting that it has been engineered for particular strengths and limitations.
Benefits of Using 1% 201% 4% Threaded Couplings
1. High Strength-to-Weight Ratio The testing and designation of a threaded coupling often lead to the development of lightweight yet robust couplings. This is especially beneficial in applications where both strength and weight savings are crucial, such as in the aerospace and automotive industries.
2. Ease of Assembly and Disassembly The threaded design allows for quick and easy assembly and disassembly of components. This is particularly useful in maintenance and repair work, where frequent access to internal components is required.
3. Versatility Threaded couplings can be designed to be compatible with a wide range of materials and sizes, making them versatile for various applications. The 1% 201% 4% designation can help engineers identify the right specifications for their needs.
4. Cost Efficiency With mass production and standardized designs, threaded couplings can be produced at a lower cost. This cost efficiency, paired with their reliability, makes them an attractive option for many engineering projects.
Conclusion
Understanding the significance of 1% 201% 4% threaded coupling is critical for engineers and designers tasked with ensuring the efficiency and reliability of mechanical systems. The application of such couplings spans across various industries, bringing together components in a secure and versatile manner. By acknowledging the specifications denoted by this designation, professionals can make informed decisions that enhance the performance and longevity of their systems. Ultimately, threaded coupling remains a cornerstone of mechanical engineering, representing the intersection of innovation, reliability, and efficiency in modern design practices.
Latest news
-
ANSI 150P SS304 SO FLANGE
NewsFeb.14,2025
-
ASTM A333GR6 STEEL PIPE
NewsJan.20,2025
-
ANSI B16.5 WELDING NECK FLANGE
NewsJan.15,2026
-
ANSI B16.5 SLIP-ON FLANGE
NewsApr.19,2024
-
SABS 1123 FLANGE
NewsJan.15,2025
-
DIN86044 PLATE FLANGE
NewsApr.19,2024
-
DIN2527 BLIND FLANGE
NewsApr.12,2024
-
JIS B2311 Butt-Welding Fittings LR/SR 45°/90° /180°Seamless/Weld
NewsApr.23,2024











