-
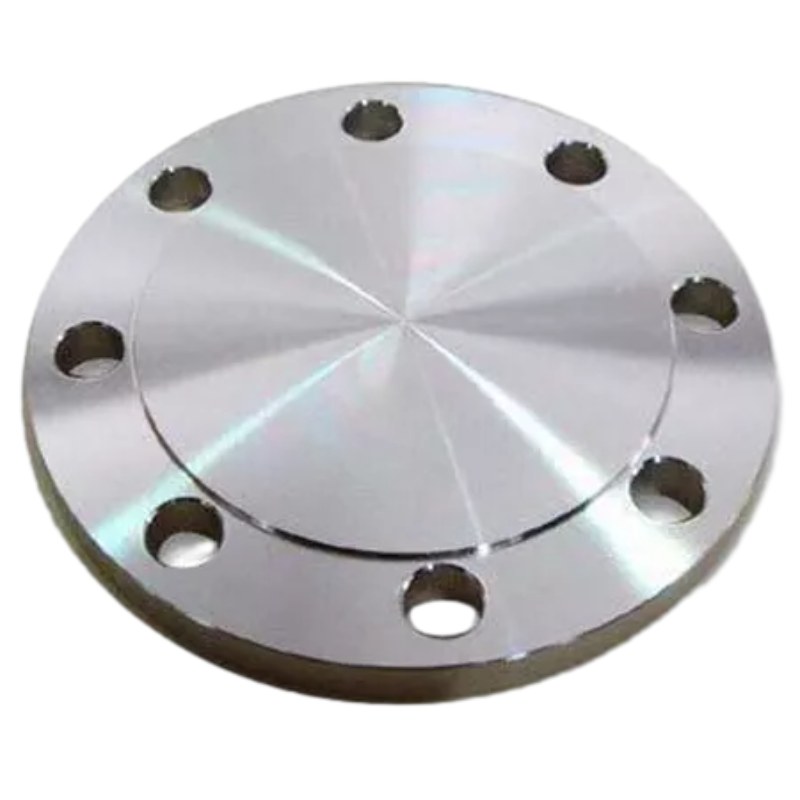
Robust Design: The GOST 12836-67 Blind Flange features a flat, circular plate with evenly spaced bolt holes around the perimeter. This design allows for easy alignment and bolting to the mating flange, providing a robust and stable closure solution for piping systems.
-
Secure Sealing: When installed at the end of a pipe, the flat face of the GOST 12836-67 Blind Flange creates a tight seal, preventing fluid leakage and maintaining the integrity of the piping system. This secure sealing capability ensures optimal performance and safety, even under extreme operating conditions.
-
Versatile Application: From oil and gas refineries to chemical processing plants and water distribution networks, GOST 12836-67 Blind Flanges find versatile application across diverse industries. Whether used for isolation purposes, pressure testing, or temporary closures, these flanges offer reliability and durability in critical piping systems.
-
Durable Construction: Constructed from high-quality materials such as carbon steel, stainless steel, or alloy steel, GOST 12836-67 Blind Flanges exhibit exceptional strength and durability. They are engineered to withstand harsh operating conditions, including corrosive environments, high temperatures, and intense pressure, ensuring long-term performance and reliability.
-
Precision Engineering: GOST 12836-67 Blind Flanges undergo precision machining and engineering processes to meet strict dimensional tolerances and surface finish requirements. This precision ensures compatibility and interchangeability with other standard flanges, facilitating seamless integration into piping systems and minimizing the risk of leaks or failures.
-
Ease of Installation: Installing GOST 12836-67 Blind Flanges is efficient and straightforward, requiring simple alignment and bolting to the pipe end. Their standardized dimensions and design facilitate easy integration into existing piping networks, minimizing installation time and labor costs.
Key Features:
- Robust design for secure closure
- Secure sealing with flat face design
- Versatile application across industries
- Durable construction for long-term performance
- Precision engineering for tight tolerances
- Ease of installation with simple alignment and bolting
Material Selection for GOST 12836-67 Blind Flanges: What You Need to Know
When it comes to GOST 12836-67 blind flanges, selecting the appropriate material is crucial for ensuring functionality, safety, and longevity in various applications. GOST standards, established by the Euro-Asian Council for Standardization, Metrology and Certification, guide the specification of materials to maintain the integrity of piping systems.
Key Considerations for Material Selection:
1. Corrosion Resistance: One of the primary factors in choosing a material for GOST blind flanges is its ability to resist corrosion. Stainless steel (such as 304, and 316) is a popular choice due to its excellent resistance to oxidizing environments. For applications involving aggressive chemicals, alloys like Inconel or Monel are often considered.
2. Pressure and Temperature Rating: GOST blind flanges need to be rated for the specific pressure and temperature conditions they will face. Material selection must align with the service conditions to avoid failure. For high-pressure applications, carbon steel flanges can be suitable, provided they are properly treated or coated.
3. Weldability and Machinability: Depending on installation requirements, the selected material should offer appropriate weldability and machinability. If modifications or on-site fabrication are necessary, choosing materials that can be easily welded is essential.
4. Standards Compliance: Ensure that the materials selected comply with all relevant GOST standards. This not only guarantees quality but also maintains compatibility within the piping system.
5. Cost-effectiveness: While material selection should prioritize performance and safety, cost considerations also play a significant role, especially in large-scale projects. Finding a balance between budget and quality is essential.
Differences Between GOST 12836-67 Blind Flange and Other Flange Standards
When comparing the GOST 12836-67 blind flange with other flange standards, several key differences emerge that reflect the unique characteristics and applications of the Russian standard. The GOST (Gosudarstvennyy Standart) system is a set of regulations and guidelines that govern various industrial products, including blind flanges, which are used to seal off piping systems.
One of the primary differences lies in the dimension and pressure rating classifications. GOST 12836-67 blind flanges are specifically designed according to Russian specifications, with dimensions that may differ significantly from those outlined in ANSI, ASME, or ISO standards. For instance, while ANSI/ASME flanges are typically categorized into nominal pipe sizes (NPS) and pressure classes, GOST flanges feature a unique set of sizes and pressure ratings, making it essential for engineers to select the appropriate type based on regional standards.
Another notable difference is the material composition. The GOST standard emphasizes the use of specific materials that are suited for the harsh Russian climate and industrial requirements. While common materials such as carbon steel and stainless steel are also used in other standards, GOST may specify additional material grades to accommodate unique environmental challenges, including extreme temperatures and corrosive conditions.
Additionally, the manufacturing and testing processes for GOST 12836-67 blind flanges are subject to local industry regulations, which might include stricter quality assurance protocols compared to other international standards. This ensures that the flanges not only meet dimensional specifications but also effectively withstand the pressures and temperatures expected in typical applications within Russia.
In summary, while GOST 12836-67 blind flanges share similarities with other flange standards, their unique dimensions, material requirements, and quality assurance processes set them apart. Understanding these differences is crucial for engineers and designers when selecting flanges for specific applications in diverse geographical locations.