-
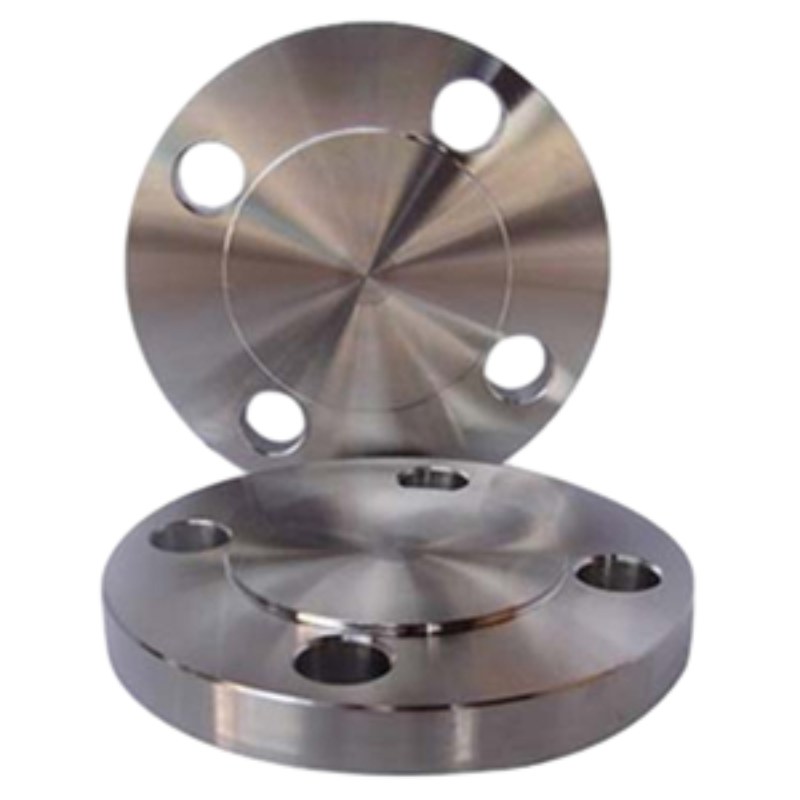
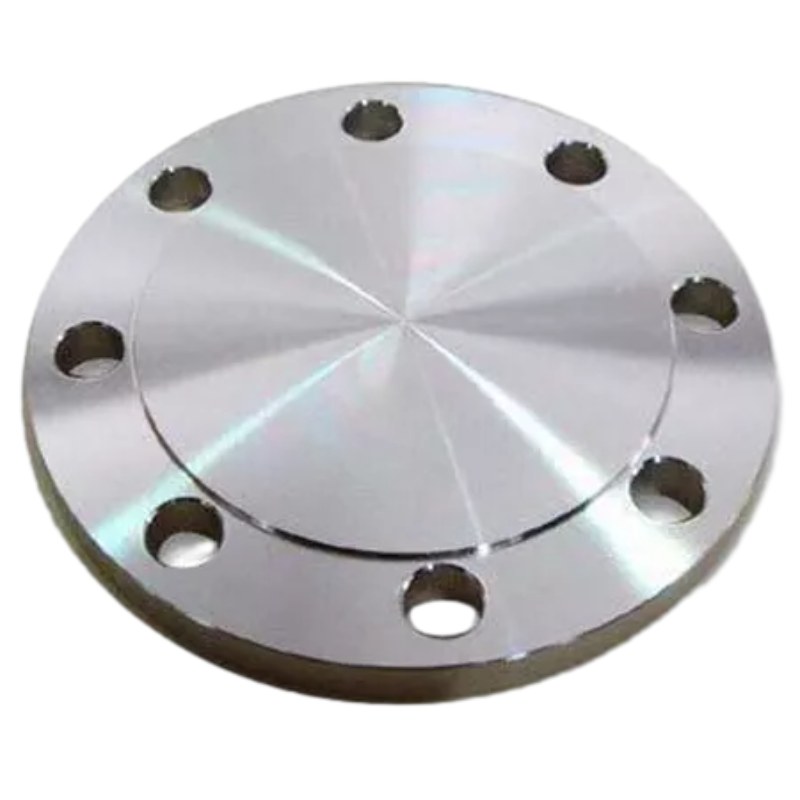
Robustný dizajn: Slepá príruba GOST 12836-67 má plochú kruhovú dosku s rovnomerne rozmiestnenými otvormi pre skrutky po obvode. Táto konštrukcia umožňuje ľahké zarovnanie a priskrutkovanie k protiprírube, čím poskytuje robustné a stabilné riešenie uzáveru pre potrubné systémy.
-
Bezpečné tesnenie: Pri inštalácii na konci potrubia vytvára ploché čelo slepej príruby GOST 12836-67 tesné tesnenie, ktoré zabraňuje úniku kvapaliny a zachováva integritu potrubného systému. Táto bezpečná tesniaca schopnosť zaisťuje optimálny výkon a bezpečnosť aj v extrémnych prevádzkových podmienkach.
-
Všestranná aplikácia: Od ropných a plynových rafinérií až po chemické spracovateľské závody a rozvodné siete vody, zaslepovacie príruby podľa GOST 12836-67 nachádzajú všestranné uplatnenie v rôznych odvetviach. Či už sa používajú na izolačné účely, tlakové skúšky alebo dočasné uzávery, tieto príruby ponúkajú spoľahlivosť a odolnosť v kritických potrubných systémoch.
-
Odolná konštrukcia: Slepé príruby GOST 12836-67, vyrobené z vysoko kvalitných materiálov, ako je uhlíková oceľ, nehrdzavejúca oceľ alebo legovaná oceľ, vykazujú výnimočnú pevnosť a odolnosť. Sú skonštruované tak, aby odolali náročným prevádzkovým podmienkam vrátane korozívneho prostredia, vysokých teplôt a intenzívneho tlaku, čím zaisťujú dlhodobý výkon a spoľahlivosť.
-
Presné strojárstvo: GOST 12836-67 Slepé príruby prechádzajú presným obrábaním a inžinierskymi procesmi, aby spĺňali prísne rozmerové tolerancie a požiadavky na povrchovú úpravu. Táto presnosť zaisťuje kompatibilitu a zameniteľnosť s inými štandardnými prírubami, čím uľahčuje bezproblémovú integráciu do potrubných systémov a minimalizuje riziko netesností alebo porúch.
-
Jednoduchosť inštalácie: Inštalácia slepých prírub podľa GOST 12836-67 je efektívna a jednoduchá a vyžaduje jednoduché zarovnanie a priskrutkovanie ku koncu potrubia. Ich štandardizované rozmery a dizajn uľahčujú jednoduchú integráciu do existujúcich potrubných sietí, čím minimalizujú čas inštalácie a náklady na prácu.
Kľúčové vlastnosti:
- Robustný dizajn pre bezpečné zatváranie
- Bezpečné tesnenie s plochým dizajnom
- Všestranné použitie v rôznych odvetviach
- Odolná konštrukcia pre dlhodobý výkon
- Presné inžinierstvo pre úzke tolerancie
- Jednoduchá inštalácia s jednoduchým vyrovnaním a skrutkovaním
Material Selection for GOST 12836-67 Blind Flanges: What You Need to Know
When it comes to GOST 12836-67 blind flanges, selecting the appropriate material is crucial for ensuring functionality, safety, and longevity in various applications. GOST standards, established by the Euro-Asian Council for Standardization, Metrology and Certification, guide the specification of materials to maintain the integrity of piping systems.
Key Considerations for Material Selection:
1. Corrosion Resistance: One of the primary factors in choosing a material for GOST blind flanges is its ability to resist corrosion. Stainless steel (such as 304, and 316) is a popular choice due to its excellent resistance to oxidizing environments. For applications involving aggressive chemicals, alloys like Inconel or Monel are often considered.
2. Pressure and Temperature Rating: GOST blind flanges need to be rated for the specific pressure and temperature conditions they will face. Material selection must align with the service conditions to avoid failure. For high-pressure applications, carbon steel flanges can be suitable, provided they are properly treated or coated.
3. Weldability and Machinability: Depending on installation requirements, the selected material should offer appropriate weldability and machinability. If modifications or on-site fabrication are necessary, choosing materials that can be easily welded is essential.
4. Standards Compliance: Ensure that the materials selected comply with all relevant GOST standards. This not only guarantees quality but also maintains compatibility within the piping system.
5. Cost-effectiveness: While material selection should prioritize performance and safety, cost considerations also play a significant role, especially in large-scale projects. Finding a balance between budget and quality is essential.
Differences Between GOST 12836-67 Blind Flange and Other Flange Standards
When comparing the GOST 12836-67 blind flange with other flange standards, several key differences emerge that reflect the unique characteristics and applications of the Russian standard. The GOST (Gosudarstvennyy Standart) system is a set of regulations and guidelines that govern various industrial products, including blind flanges, which are used to seal off piping systems.
One of the primary differences lies in the dimension and pressure rating classifications. GOST 12836-67 blind flanges are specifically designed according to Russian specifications, with dimensions that may differ significantly from those outlined in ANSI, ASME, or ISO standards. For instance, while ANSI/ASME flanges are typically categorized into nominal pipe sizes (NPS) and pressure classes, GOST flanges feature a unique set of sizes and pressure ratings, making it essential for engineers to select the appropriate type based on regional standards.
Another notable difference is the material composition. The GOST standard emphasizes the use of specific materials that are suited for the harsh Russian climate and industrial requirements. While common materials such as carbon steel and stainless steel are also used in other standards, GOST may specify additional material grades to accommodate unique environmental challenges, including extreme temperatures and corrosive conditions.
Additionally, the manufacturing and testing processes for GOST 12836-67 blind flanges are subject to local industry regulations, which might include stricter quality assurance protocols compared to other international standards. This ensures that the flanges not only meet dimensional specifications but also effectively withstand the pressures and temperatures expected in typical applications within Russia.
In summary, while GOST 12836-67 blind flanges share similarities with other flange standards, their unique dimensions, material requirements, and quality assurance processes set them apart. Understanding these differences is crucial for engineers and designers when selecting flanges for specific applications in diverse geographical locations.