-
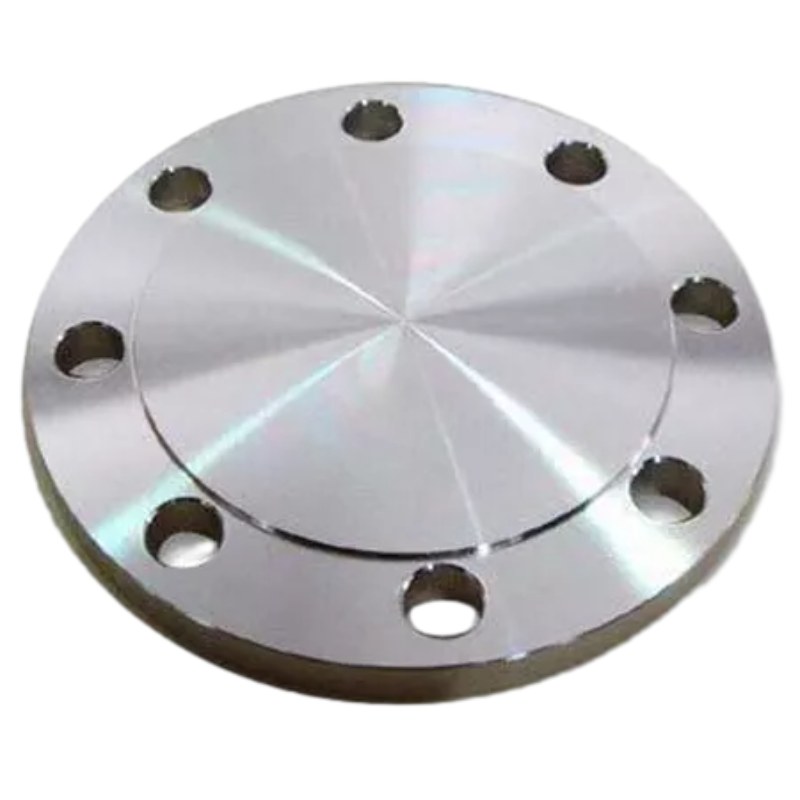
Desain Kuat: Flensa Buta GOST 12836-67 dilengkapi dengan pelat bundar datar dengan lubang baut dengan jarak yang sama di sekelilingnya. Desain ini memudahkan penyelarasan dan pemasangan baut ke flensa pasangan, memberikan solusi penutupan yang kuat dan stabil untuk sistem perpipaan.
-
Penyegelan Aman: Saat dipasang di ujung pipa, permukaan datar Flange Buta GOST 12836-67 menciptakan segel yang rapat, mencegah kebocoran cairan dan menjaga integritas sistem perpipaan. Kemampuan penyegelan yang aman ini memastikan kinerja dan keamanan optimal, bahkan dalam kondisi pengoperasian yang ekstrem.
-
Aplikasi Serbaguna: Dari kilang minyak dan gas hingga pabrik pemrosesan kimia dan jaringan distribusi air, Flensa Buta GOST 12836-67 dapat diterapkan secara serbaguna di beragam industri. Baik digunakan untuk tujuan isolasi, pengujian tekanan, atau penutupan sementara, flensa ini menawarkan keandalan dan daya tahan dalam sistem perpipaan penting.
-
Konstruksi Tahan Lama: Dibangun dari bahan berkualitas tinggi seperti baja karbon, baja tahan karat, atau baja paduan, Flensa Buta GOST 12836-67 menunjukkan kekuatan dan daya tahan yang luar biasa. Mereka dirancang untuk tahan terhadap kondisi pengoperasian yang keras, termasuk lingkungan korosif, suhu tinggi, dan tekanan kuat, sehingga memastikan kinerja dan keandalan jangka panjang.
-
Rekayasa Presisi: GOST 12836-67 Flensa Buta menjalani proses pemesinan dan rekayasa presisi untuk memenuhi toleransi dimensi yang ketat dan persyaratan penyelesaian permukaan. Ketepatan ini memastikan kompatibilitas dan pertukaran dengan flensa standar lainnya, memfasilitasi integrasi tanpa batas ke dalam sistem perpipaan dan meminimalkan risiko kebocoran atau kegagalan.
-
Kemudahan Instalasi: Memasang Flensa Buta GOST 12836-67 efisien dan mudah, memerlukan penyelarasan sederhana dan pemasangan baut ke ujung pipa. Dimensi dan desain standarnya memudahkan integrasi ke dalam jaringan perpipaan yang ada, meminimalkan waktu pemasangan dan biaya tenaga kerja.
Fitur Utama:
- Desain yang kuat untuk penutupan yang aman
- Penyegelan aman dengan desain muka datar
- Aplikasi serbaguna di seluruh industri
- Konstruksi tahan lama untuk kinerja jangka panjang
- Rekayasa presisi untuk toleransi yang ketat
- Kemudahan pemasangan dengan penyelarasan dan perbautan sederhana
Material Selection for GOST 12836-67 Blind Flanges: What You Need to Know
When it comes to GOST 12836-67 blind flanges, selecting the appropriate material is crucial for ensuring functionality, safety, and longevity in various applications. GOST standards, established by the Euro-Asian Council for Standardization, Metrology and Certification, guide the specification of materials to maintain the integrity of piping systems.
Key Considerations for Material Selection:
1. Corrosion Resistance: One of the primary factors in choosing a material for GOST blind flanges is its ability to resist corrosion. Stainless steel (such as 304, and 316) is a popular choice due to its excellent resistance to oxidizing environments. For applications involving aggressive chemicals, alloys like Inconel or Monel are often considered.
2. Pressure and Temperature Rating: GOST blind flanges need to be rated for the specific pressure and temperature conditions they will face. Material selection must align with the service conditions to avoid failure. For high-pressure applications, carbon steel flanges can be suitable, provided they are properly treated or coated.
3. Weldability and Machinability: Depending on installation requirements, the selected material should offer appropriate weldability and machinability. If modifications or on-site fabrication are necessary, choosing materials that can be easily welded is essential.
4. Standards Compliance: Ensure that the materials selected comply with all relevant GOST standards. This not only guarantees quality but also maintains compatibility within the piping system.
5. Cost-effectiveness: While material selection should prioritize performance and safety, cost considerations also play a significant role, especially in large-scale projects. Finding a balance between budget and quality is essential.
Differences Between GOST 12836-67 Blind Flange and Other Flange Standards
When comparing the GOST 12836-67 blind flange with other flange standards, several key differences emerge that reflect the unique characteristics and applications of the Russian standard. The GOST (Gosudarstvennyy Standart) system is a set of regulations and guidelines that govern various industrial products, including blind flanges, which are used to seal off piping systems.
One of the primary differences lies in the dimension and pressure rating classifications. GOST 12836-67 blind flanges are specifically designed according to Russian specifications, with dimensions that may differ significantly from those outlined in ANSI, ASME, or ISO standards. For instance, while ANSI/ASME flanges are typically categorized into nominal pipe sizes (NPS) and pressure classes, GOST flanges feature a unique set of sizes and pressure ratings, making it essential for engineers to select the appropriate type based on regional standards.
Another notable difference is the material composition. The GOST standard emphasizes the use of specific materials that are suited for the harsh Russian climate and industrial requirements. While common materials such as carbon steel and stainless steel are also used in other standards, GOST may specify additional material grades to accommodate unique environmental challenges, including extreme temperatures and corrosive conditions.
Additionally, the manufacturing and testing processes for GOST 12836-67 blind flanges are subject to local industry regulations, which might include stricter quality assurance protocols compared to other international standards. This ensures that the flanges not only meet dimensional specifications but also effectively withstand the pressures and temperatures expected in typical applications within Russia.
In summary, while GOST 12836-67 blind flanges share similarities with other flange standards, their unique dimensions, material requirements, and quality assurance processes set them apart. Understanding these differences is crucial for engineers and designers when selecting flanges for specific applications in diverse geographical locations.